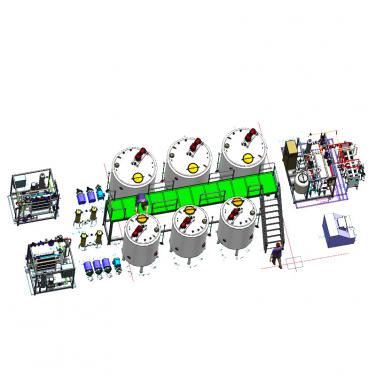
A complete and successful milk processing line can efficiently produce milk related products, and complete the integrated workflow from raw materials to packaging. Through a variety of different milk processing equipment, milk can be produced quickly. It not only connects various mechanical equipment, but also achieves a high degree of system integration from the software.
Today, let's talk about the design idea of the processing line of the pasteurization plant of whole milk, discuss the key points in the design of the milk processing line, master the method of integrating different equipment, and discuss the process of milk production and various possible problems.
The milk processing line will encounter various problems in the actual production process. Our milk processing line should be able to find these problems in time and solve them quickly. For example:
Product related - about the quality of raw materials, processing and final products
Process related – regarding plant capacity, selection and compatibility of components, degree of process control, availability of heating and cooling media, cleaning of processing equipment, etc.
Economy - the total production cost of meeting the specified quality standards is as low as possible
Law - legislation that defines process parameters and the choice of component and system solutions
In most countries that process milk into various products, the law stipulates certain requirements to protect consumers from pathogenic microorganisms. The wording and recommendations may vary, but the following combinations cover the most common requirements:
heat treatment
Milk must be heat treated in a manner that kills all pathogenic microorganisms. The minimum temperature of 72 ° C / holding time of 15 seconds must be reached.
The heating temperature must be recorded automatically and the transcript must be kept within the specified time.
Clarification before heat treatment
Since milk usually contains solid substances, such as dirt particles, white blood cells (white blood cells) and somatic cells (breast tissue), it must be clarified. Since pasteurization is unlikely to be effective if bacteria are hidden in lumps and particles in milk, it must be clarified before heating. Milk can be clarified in a filter or more effectively in a centrifugal clarifier.
The heat exchanger has been calculated, so a higher pressure should be used
It remains in the pasteurized milk stream compared to non pasteurized milk and service media. If leakage occurs in the heat exchanger, pasteurized milk must flow into milk or cooling medium that has not been pasteurized, and must not flow in the opposite direction. In order to ensure this, it is usually necessary to use booster pump to generate differential pressure, which is mandatory in some countries.
If the temperature of pasteurization products drops due to the temporary shortage of heating medium, the factory must be equipped with a shunt valve to divert the milk that is not heated enough back to the balance tank.
The remote control process requires the following equipment:
Silo for storing raw milk.
Plate heat exchanger, insulation pipe and hot water unit for heating and cooling.
Centrifugal clarifier (since only whole milk is processed, centrifugal separator is not required in this case).
Intermediate storage tank is used for temporary storage of processed milk.
Pipes and fittings for connecting main components and pneumatic valves for controlling and distributing product flow and cleaning fluid.
A pump used to transport milk through the entire milk processing plant.
Control equipment for controlling capacity, pasteurization temperature and valve position.
Various service systems:
– water supply
– steam production
– coolant cooling
– compressed air for pneumatic devices
– electricity
– drainage and waste water.
The service media requirements are calculated after the factory design is agreed. Therefore, it is necessary to know the temperature sequence of pasteurization and the specifications of all other areas that need heating and cooling (refrigeration, cleaning system, etc.) before determining the number and power of electric machines, the number of pneumatic machines, the operating units, the working hours of the factory, etc. This book does not cover such calculations.
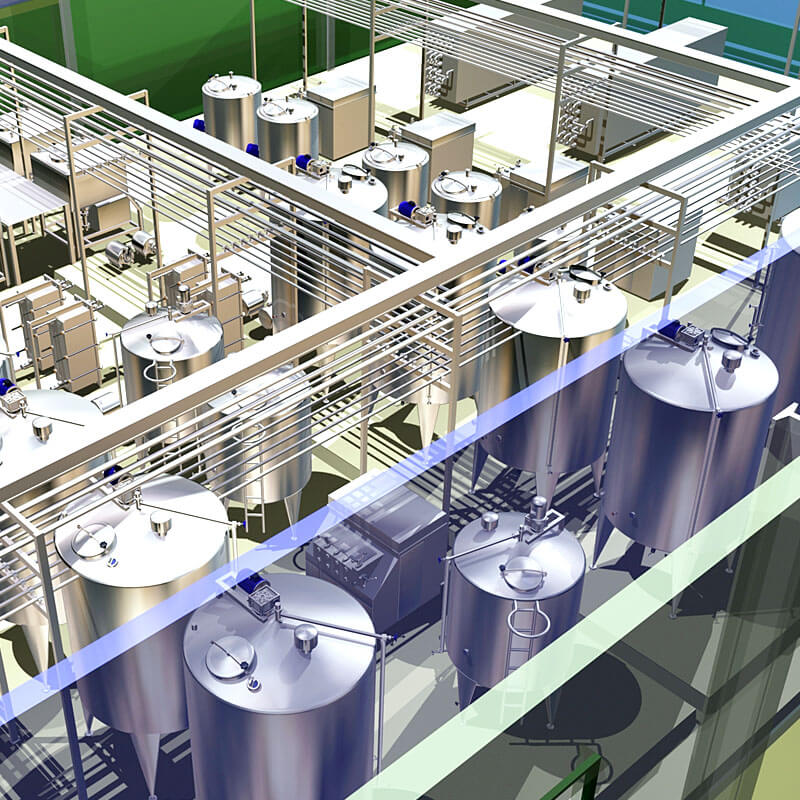
Silo tank
The number and size of silos depend on the delivery plan of raw milk and the volume of each delivery. In order to make the factory operate continuously without shutdown due to lack of raw materials, there must be an adequate supply of raw milk.
Preferably, the milk should have been stored for at least one hour before processing, because during this time the milk will naturally degass. Short time mixing is acceptable, but it is not really necessary to mix until about 5-10 minutes before emptying the silo to balance the overall mass. This avoids interference with the natural degassing process.
The main purpose of pasteurization of milk is to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms. For this purpose, milk is usually heated to not less than 72 ° C for at least 15 seconds, and then cooled rapidly. The laws of many countries stipulate these parameters. Plate heat exchangers are most commonly used in pasteurization of milk in the market. When long-term operation is required, tubular heat exchangers can be used. Scraping heat exchanger is used for viscous products.
In the plate heat exchanger, the connecting plate between each part is provided with the inlet and outlet of product and service medium. The inlet and outlet connections can be oriented vertically or horizontally. The ends of plate heat exchangers (frames and pressure plates) can also be equipped with inlets and outlets.
When long-term operation is required, the tubular heat exchanger is a substitute for the plate heat exchanger.
Hot water or saturated steam under atmospheric pressure can be used as the heating medium in pasteurizer. However, due to the large temperature difference, hot steam is not used. Therefore, the most commonly used heating medium is hot water, which is usually about 2 – 3 ° C higher than the temperature required for the product.
Steam is delivered from the steam boiler at a pressure of 600 – 700 kPa (6 – 7 bar). The steam is used to heat the water and then heat the product to pasteurization temperature.
The temperature controller acts on the steam regulating valve to maintain a constant pasteurization temperature. Any trend of product temperature decline will be immediately detected by the sensor in the product line before the holding tube. The sensor then changes the signal to the controller, which opens the steam regulating valve to supply more steam to the water. This will raise the temperature of the circulating water and prevent the temperature drop in the product.
The length and size of the holding pipe located outside are calculated based on the known holding time, the hourly capacity of the equipment and the pipe size, which are usually the same as the pipes supplying pasteurization equipment. Usually, the holding tube is covered with a stainless steel cover to prevent people from being burned and radiation when touching it.
Milk must be pasteurized properly before leaving the plate heat exchanger. If the temperature drops below 72 ° C, milk that has not been pasteurized must be stored separately from products that have been pasteurized. For this purpose, the temperature transmitter and shunt valve are installed in the pipeline downstream of the insulation pipe. If the temperature transmitter detects that the milk passing through it is not fully heated, return the unpasteurized milk to the balancing tank.